Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Comparing initial point generation methods#
Holger Nahrstaedt 2020
Bayesian optimization or sequential model-based optimization uses a surrogate
model to model the expensive to evaluate function func. There are several
choices for what kind of surrogate model to use. This notebook compares the
performance of:
Halton sequence,
Hammersly sequence,
Sobol’ sequence and
Latin hypercube sampling
as initial points. The purely random point generation is used as a baseline.
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(123)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skopt.benchmarks import hart6 as hart6_
Toy model#
We will use the benchmarks.hart6 function as toy model for the expensive function.
In a real world application this function would be unknown and expensive
to evaluate.
# redefined `hart6` to allow adding arbitrary "noise" dimensions
def hart6(x, noise_level=0.0):
return hart6_(x[:6]) + noise_level * np.random.randn()
from skopt.benchmarks import branin as _branin
def branin(x, noise_level=0.0):
return _branin(x) + noise_level * np.random.randn()
import time
from matplotlib.pyplot import cm
from skopt import gp_minimize
def plot_convergence(
result_list, true_minimum=None, yscale=None, title="Convergence plot"
):
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_title(title)
ax.set_xlabel("Number of calls $n$")
ax.set_ylabel(r"$\min f(x)$ after $n$ calls")
ax.grid()
if yscale is not None:
ax.set_yscale(yscale)
colors = cm.hsv(np.linspace(0.25, 1.0, len(result_list)))
for results, color in zip(result_list, colors):
name, results = results
n_calls = len(results[0].x_iters)
iterations = range(1, n_calls + 1)
mins = [[np.min(r.func_vals[:i]) for i in iterations] for r in results]
ax.plot(iterations, np.mean(mins, axis=0), c=color, label=name)
# ax.errorbar(iterations, np.mean(mins, axis=0),
# yerr=np.std(mins, axis=0), c=color, label=name)
if true_minimum:
ax.axhline(true_minimum, linestyle="--", color="r", lw=1, label="True minimum")
ax.legend(loc="best")
return ax
def run(minimizer, initial_point_generator, n_initial_points=10, n_repeats=1):
return [
minimizer(
func,
bounds,
n_initial_points=n_initial_points,
initial_point_generator=initial_point_generator,
n_calls=n_calls,
random_state=n,
)
for n in range(n_repeats)
]
def run_measure(initial_point_generator, n_initial_points=10):
start = time.time()
# n_repeats must set to a much higher value to obtain meaningful results.
n_repeats = 1
res = run(
gp_minimize,
initial_point_generator,
n_initial_points=n_initial_points,
n_repeats=n_repeats,
)
duration = time.time() - start
print("%s: %.2f s" % (initial_point_generator, duration))
return res
Objective#
The objective of this example is to find one of these minima in as
few iterations as possible. One iteration is defined as one call
to the benchmarks.hart6 function.
We will evaluate each model several times using a different seed for the random number generator. Then compare the average performance of these models. This makes the comparison more robust against models that get “lucky”.
from functools import partial
example = "hart6"
if example == "hart6":
func = partial(hart6, noise_level=0.1)
bounds = [
(0.0, 1.0),
] * 6
true_minimum = -3.32237
n_calls = 30
n_initial_points = 10
yscale = None
title = "Convergence plot - hart6"
else:
func = partial(branin, noise_level=2.0)
bounds = [(-5.0, 10.0), (0.0, 15.0)]
true_minimum = 0.397887
n_calls = 30
n_initial_points = 10
yscale = "log"
title = "Convergence plot - branin"
from skopt.utils import cook_initial_point_generator
# Random search
dummy_res = run_measure("random", n_initial_points)
lhs = cook_initial_point_generator("lhs", lhs_type="classic", criterion=None)
lhs_res = run_measure(lhs, n_initial_points)
lhs2 = cook_initial_point_generator("lhs", criterion="maximin")
lhs2_res = run_measure(lhs2, n_initial_points)
sobol = cook_initial_point_generator("sobol", randomize=False, min_skip=1, max_skip=100)
sobol_res = run_measure(sobol, n_initial_points)
halton_res = run_measure("halton", n_initial_points)
hammersly_res = run_measure("hammersly", n_initial_points)
grid_res = run_measure("grid", n_initial_points)
random: 11.50 s
<skopt.sampler.lhs.Lhs object at 0x0000020BCFA298D0>: 10.31 s
<skopt.sampler.lhs.Lhs object at 0x0000020BCF824250>: 10.83 s
D:\git\scikit-optimize\skopt\sampler\sobol.py:521: UserWarning: The balance properties of Sobol' points require n to be a power of 2. 0 points have been previously generated, then: n=0+10=10.
warnings.warn(
<skopt.sampler.sobol.Sobol object at 0x0000020BCFAF0210>: 8.19 s
halton: 5.61 s
hammersly: 6.14 s
grid: 11.66 s
Note that this can take a few minutes.
plot = plot_convergence(
[
("random", dummy_res),
("lhs", lhs_res),
("lhs_maximin", lhs2_res),
("sobol'", sobol_res),
("halton", halton_res),
("hammersly", hammersly_res),
("grid", grid_res),
],
true_minimum=true_minimum,
yscale=yscale,
title=title,
)
plt.show()
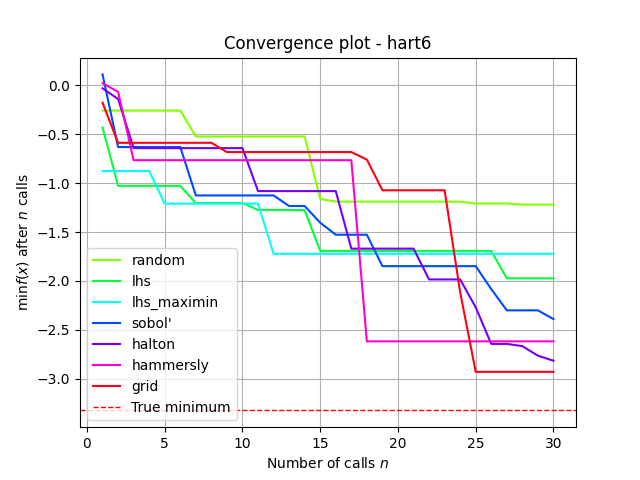
This plot shows the value of the minimum found (y axis) as a function
of the number of iterations performed so far (x axis). The dashed red line
indicates the true value of the minimum of the benchmarks.hart6
function.
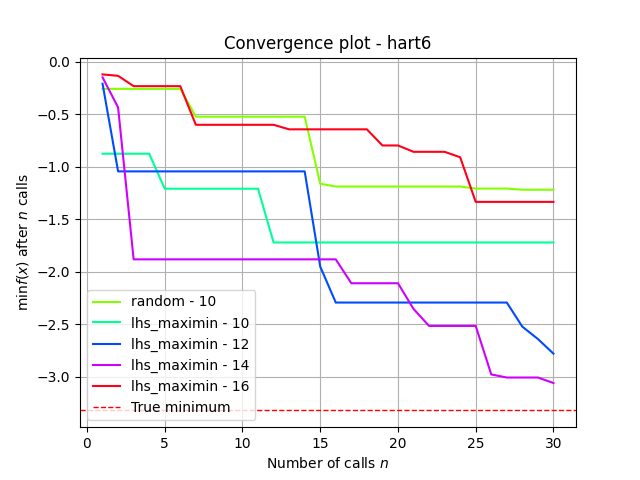
Test with different n_random_starts values
lhs2 = cook_initial_point_generator("lhs", criterion="maximin")
lhs2_15_res = run_measure(lhs2, 12)
lhs2_20_res = run_measure(lhs2, 14)
lhs2_25_res = run_measure(lhs2, 16)
<skopt.sampler.lhs.Lhs object at 0x0000020BD8E162D0>: 5.83 s
<skopt.sampler.lhs.Lhs object at 0x0000020BD8E162D0>: 5.66 s
<skopt.sampler.lhs.Lhs object at 0x0000020BD8E162D0>: 4.54 s
n_random_starts = 10 produces the best results
plot = plot_convergence(
[
("random - 10", dummy_res),
("lhs_maximin - 10", lhs2_res),
("lhs_maximin - 12", lhs2_15_res),
("lhs_maximin - 14", lhs2_20_res),
("lhs_maximin - 16", lhs2_25_res),
],
true_minimum=true_minimum,
yscale=yscale,
title=title,
)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 20.489 seconds)
