Note
Go to the end to download the full example code or to run this example in your browser via Binder
Use different base estimators for optimization#
Sigurd Carlen, September 2019. Reformatted by Holger Nahrstaedt 2020
To use different base_estimator or create a regressor with different parameters, we can create a regressor object and set it as kernel.
This example uses plots.plot_gaussian_process which is available
since version 0.8.
print(__doc__)
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(1234)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skopt import Optimizer
from skopt.plots import plot_gaussian_process
Toy example#
Let assume the following noisy function \(f\):
noise_level = 0.1
# Our 1D toy problem, this is the function we are trying to
# minimize
def objective(x, noise_level=noise_level):
return np.sin(5 * x[0]) * (1 - np.tanh(x[0] ** 2)) + np.random.randn() * noise_level
def objective_wo_noise(x):
return objective(x, noise_level=0)
opt_gp = Optimizer(
[(-2.0, 2.0)],
base_estimator="GP",
n_initial_points=5,
acq_optimizer="sampling",
random_state=42,
)
def plot_optimizer(res, n_iter, max_iters=5):
if n_iter == 0:
show_legend = True
else:
show_legend = False
ax = plt.subplot(max_iters, 2, 2 * n_iter + 1)
# Plot GP(x) + contours
ax = plot_gaussian_process(
res,
ax=ax,
objective=objective_wo_noise,
noise_level=noise_level,
show_legend=show_legend,
show_title=True,
show_next_point=False,
show_acq_func=False,
)
ax.set_ylabel("")
ax.set_xlabel("")
if n_iter < max_iters - 1:
ax.get_xaxis().set_ticklabels([])
# Plot EI(x)
ax = plt.subplot(max_iters, 2, 2 * n_iter + 2)
ax = plot_gaussian_process(
res,
ax=ax,
noise_level=noise_level,
show_legend=show_legend,
show_title=False,
show_next_point=True,
show_acq_func=True,
show_observations=False,
show_mu=False,
)
ax.set_ylabel("")
ax.set_xlabel("")
if n_iter < max_iters - 1:
ax.get_xaxis().set_ticklabels([])
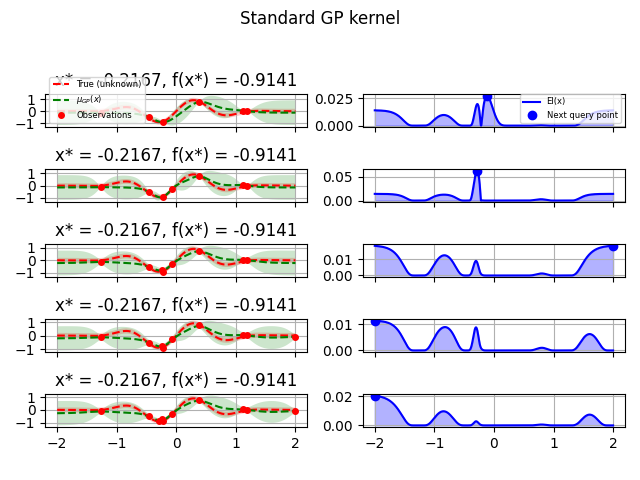
GP kernel#
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle("Standard GP kernel")
for i in range(10):
next_x = opt_gp.ask()
f_val = objective(next_x)
res = opt_gp.tell(next_x, f_val)
if i >= 5:
plot_optimizer(res, n_iter=i - 5, max_iters=5)
plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0.03, 1, 0.95])
plt.plot()
[]
Test different kernels#
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import (
RBF,
ConstantKernel,
DotProduct,
ExpSineSquared,
Matern,
RationalQuadratic,
)
from skopt.learning import GaussianProcessRegressor
from skopt.learning.gaussian_process.kernels import ConstantKernel, Matern
# Gaussian process with Matérn kernel as surrogate model
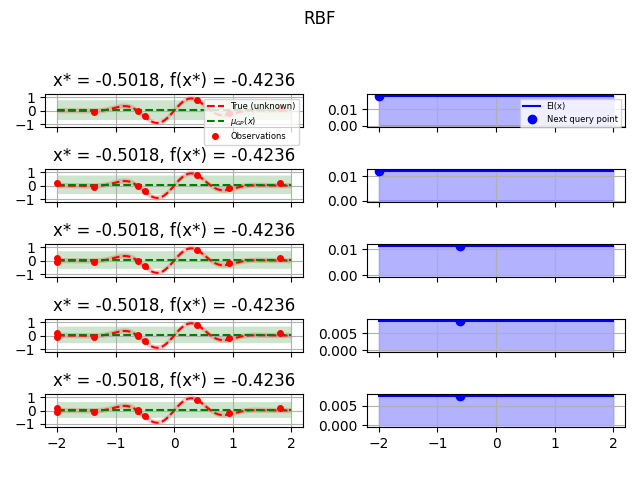
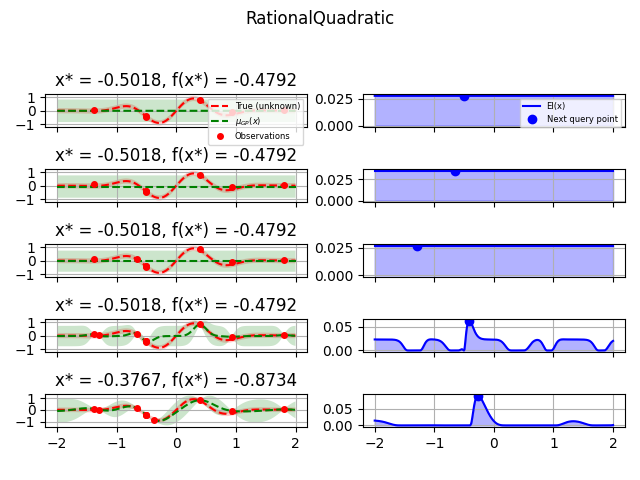
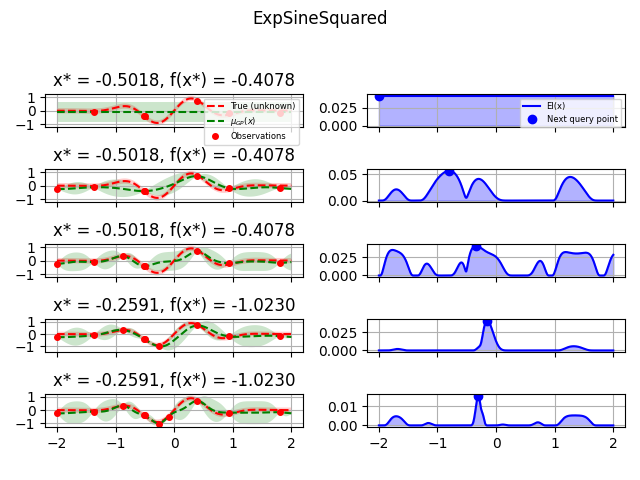
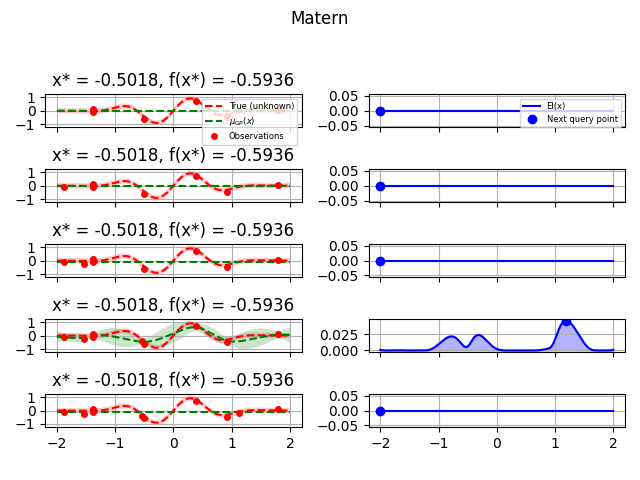
kernels = [
(1.0 * RBF(length_scale=1.0, length_scale_bounds=(1e-1, 10.0)), "RBF"),
(1.0 * RationalQuadratic(length_scale=1.0, alpha=0.1), "RationalQuadratic"),
(1.0
* ExpSineSquared(
length_scale=1.0,
periodicity=3.0,
length_scale_bounds=(0.1, 10.0),
periodicity_bounds=(1.0, 10.0),
), "ExpSineSquared"),
# (ConstantKernel(0.1, (0.01, 10.0))
# * (DotProduct(sigma_0=1.0, sigma_0_bounds=(0.1, 10.0)) ** 2), "ConstantKernel"),
(1.0 * Matern(length_scale=1.0, length_scale_bounds=(1e-1, 10.0), nu=2.5), "Matern"),
]
for kernel, label in kernels:
gpr = GaussianProcessRegressor(
kernel=kernel,
alpha=noise_level**2,
normalize_y=True,
noise="gaussian",
n_restarts_optimizer=2,
)
opt = Optimizer(
[(-2.0, 2.0)],
base_estimator=gpr,
n_initial_points=5,
acq_optimizer="sampling",
random_state=42,
)
fig = plt.figure()
fig.suptitle(label)
for i in range(10):
next_x = opt.ask()
f_val = objective(next_x)
res = opt.tell(next_x, f_val)
if i >= 5:
plot_optimizer(res, n_iter=i - 5, max_iters=5)
plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0.03, 1, 0.95])
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 13.506 seconds)